The Ultimate Craft Hidden in Daily Life: A Journey Through Roll-to-Roll Coating Technology
2025.05.29You use your smartphone every day to post on social media or send messages. You undoubtedly protect your car with UV-blocking, heat-insulating film. Every food item you bring home from the convenience store is sealed behind a barrier layer. And in hospitals, you see a variety of medical dressings. These everyday items may seem unremarkable, but behind them lies a highly sophisticated coating process.
According to global survey data, the application scope of roll-to-roll coating equipment is expanding rapidly. By 2026, market share is estimated roughly as follows:

Consumer electronics: including flexible displays and sensors, widely used in smartphones, wearables, e-readers, touch panels, etc.;
Automotive: advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), various UV-blocking and heat-insulating coatings on windows, and the increasingly popular PPF(paint protection films)
Packaging: barrier films and security labels for electronics and food products;
Decorative and functional films: for anti-static, antimicrobial, or surface-hardening applications (e.g., screen protectors);
Other: energy storage batteries (lithium-ion and thin-film electrodes) and medical dressings.
Read more: Enhance PPF Quality: Focus on TPU Film Coating Production and Composition

Coating processes are applied in a variety of industries.
Substrates and Coating Formulations
Coating means applying a formulation evenly onto a chosen substrate, then drying and/or curing it to achieve its intended function. Thus, in roll-to-roll processes, both the substrate and the formulation critically determine coating quality.
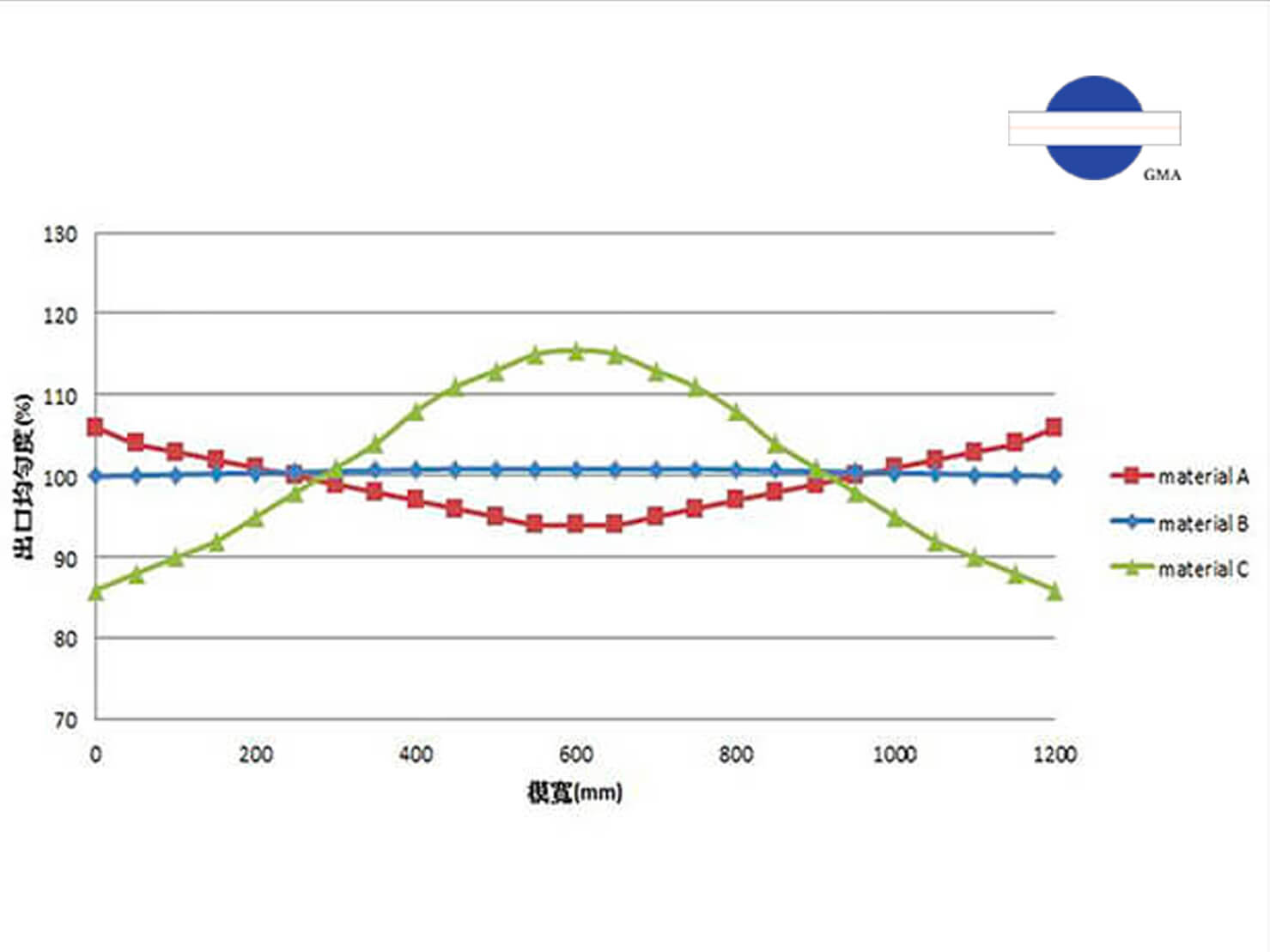
Substrate factors: uniform thickness, web tension, elasticity, and any prior surface treatment all influence coating performance. For example, large thickness tolerances can cause localized buildup and uneven film, while wrinkles, edge curl, or entrapped air—symptoms of uneven tension—make the process harder to control.
Formulation factors: viscosity, solids content, particle size and distribution, and solvent evaporation rate drive the design of both the coating head and the drying section, and ultimately govern coating quality. High-viscosity materials tend to leave visible streaks, so slot-die systems must compensate through careful hardware design. High-solids formulations are prone to cracking, so oven design and process settings must be matched accordingly.

Substrates and coating formulations are among the key factors that determine coating quality.
In short, formulation viscosity and substrate flatness affect wet- and dry-film smoothness; solvent evaporation and solids content dictate oven design and longitudinal/transverse quality; and substrate flexibility influences tension control and winding behavior.
Coating Technologies: Coater and Drying/Curing
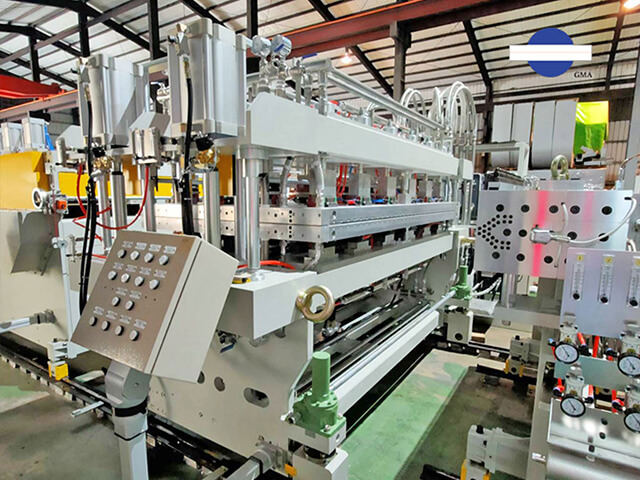
To meet diverse market needs, roll-to-roll lines often feature multiple coater .By combining different techniques on one line, operators can handle a variety of formulations and thicknesses, saving time and cost. For example, a multiple coater is equipped with slot-die, comma-roll, and gravure, it can be used for electrode coatings: slot-die for uniform thin films (10–50 µm), comma for thicker layers, and gravure for barrier or functional layers. In PPF production, slot-die creates an ultra-thin, highly transparent protective layer; gravure applies an intermediate isolation layer; and comma deposits the pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA) for the right balance of adhesion and re-positionability.
Slot-Die Coating is ideal for ultra-thin, high-uniformity films across a broad viscosity range. Though cleaning takes time, it remains the mainstream technology.
Gravure Coating excels at particle-laden or patterned, large-area coatings.
Comma for Coating handles mid-thickness, high-viscosity formulations.
Read more: From Principles to Applications: A Comprehensive Analysis of Slot Die Coating

A multi coater enables users to switch between different coating methods, saving both cost and time.
The oven on an R2R line must both dry and cure—drying removes solvents or water to convert wet film into dry film, while curing triggers polymerization to enhance hardness, adhesion, or other mechanical properties.
Common drying methods:
Hot-air drying: suitable for solvent-based (PVC, PU) and water-based systems; simple operation, broad applicability; temperature control and heat recovery can reduce energy use.
Infrared (IR) drying: rapid, localized heating for solvent-based or low-moisture PU coatings; matching wavelength to coating absorption is critical.

Hot-air drying is the most common drying method
Common curing methods:
UV curing: fast, low-energy—requires photoinitiators and a translucent substrate; safety measures are essential.
Electron-beam (EB) curing: high-solids, deep penetration; expensive equipment and radiation shielding are required.
Microwave/RF curing: fast for water-based resins, but the substrate must absorb microwaves and sensitive electronics nearby may be affected.
Ambient (natural) curing: for high-solids or thermosetting systems; takes hours to days and is sensitive to temperature and humidity.
Smart Manufacturing & Quality Control
To achieve ever-tighter tolerances, modern R2R lines incorporate auxiliary systems alongside core hardware, balancing automation with stability. Typical quality-control instruments include: In-line tension sensors、Non-contact thickness gauges、Defect-inspection cameras.
Connecting these to an MES or digital-twin platform enables adaptive tuning via machine-learning algorithms, simulates process changes, and tracks every roll’s production parameters and inspection results.
Future Trends & R2R investment
Notable developments include: Ultrathin, multifunctional coatings (e.g., nano-coatings)、Eco-friendly materials and High-speed, wide-web capacity
Why invest on R2R coating equipment:
Cross-industry versatility: one platform for automotive films, barrier films, medical dressings, etc.
Modular design: interchangeable coating heads and auxiliary modules for swift product changeovers, saving time and cost.
Consistent quality: modular structures and system support make it easy to maintain uniform output, even when switching processes.

Roll-to-roll equipment is the most worthwhile investment in the coating process.
Before investing, pay special attention to:
Formulation evaluation: identify solids content, photoinitiator needs, heat resistance, etc.
Lab-scale testing: measure drying speed, cure degree, adhesion, and surface smoothness.
Pilot trials: run extended, multi-batch tests on a small-scale line to assess stability and defect rates.
Cost analysis: calculate equipment investment, energy use, maintenance, and throughput alignment.
Read more : Want to enhance R2R coating quality? You must to know SMART rules.

Laboratory testing can help evaluate performance before investing in equipment.
Coating processes are an advanced technology hidden within everyday consumer goods, yet they are the key to achieving functionality and consistent quality. Roll-to-roll coating will continue to drive cross-industry innovation and deliver greater value in quality control and smart manufacturing. By rigorously managing every stage before implementation, you can imbue your products with the precision, efficiency, and reliability that superior coating provides.