Say Goodbye to Guesswork: Industrial AI Makes Die Design Faster, More Accurate Stable
2025.12.01At the end of 2022, the rapid emergence of OpenAI’s ChatGPT reshaped global perceptions of artificial intelligence. What began as an accessible tool for individuals quickly evolved into a collaborative enabler across industries. Today, AI significantly enhances work efficiency, precision, and speed.
Yet the impact of AI extends far beyond personal productivity. Its industrial applications are transforming how entire manufacturing ecosystems operate. While companies like NVIDIA are well known for their AI technologies, misunderstandings about AI’s actual role in manufacturing remain widespread.

AI is transforming both individuals and industries, yet many people still hold significant misconceptions about how AI is applied in the industrial field.
Many assume that AI can automatically control parameters, self-adjust systems, or independently determine solutions once data is provided. In reality, these functions belong to **automation**, not AI. Others believe that simply feeding large amounts of data into a model allows AI to find problems and deliver the best answers. But AI can only recognize **patterns**—it does not inherently understand **causality**.
In many cases, sensors, control programs, algorithms, and automated workflows are mislabeled as “AI,” even though they do not meet the criteria of true industrial intelligence.

Industrial AI must possess the core capabilities to identify patterns, build models, and provide optimized solutions.
The Three Core Capabilities of Industrial AI
To qualify as *Industrial AI*, a system must demonstrate the ability to:
- “Identify consistent patterns” within production databases including pressure, temperature, speed, and other process variables.
- ”Predict potential outcomes”, such as estimating equipment wear or identifying conditions that may lead to instability.
- ”Generate optimization strategies”, such as determining ideal production settings that deliver maximum output with minimum energy consumption.
Traditionally, these capabilities relied on rich experienced engineers who performed long-term observation, comparison, and analysis. However, time constraints, skill gaps, and the inherent subjectivity of “experience-based decision-making” make it difficult to achieve consistency and knowledge transfer. This is one of the key reasons why more manufacturers are now integrating **Industrial AI** into their workflows—not to replace professionals, but to empower them.
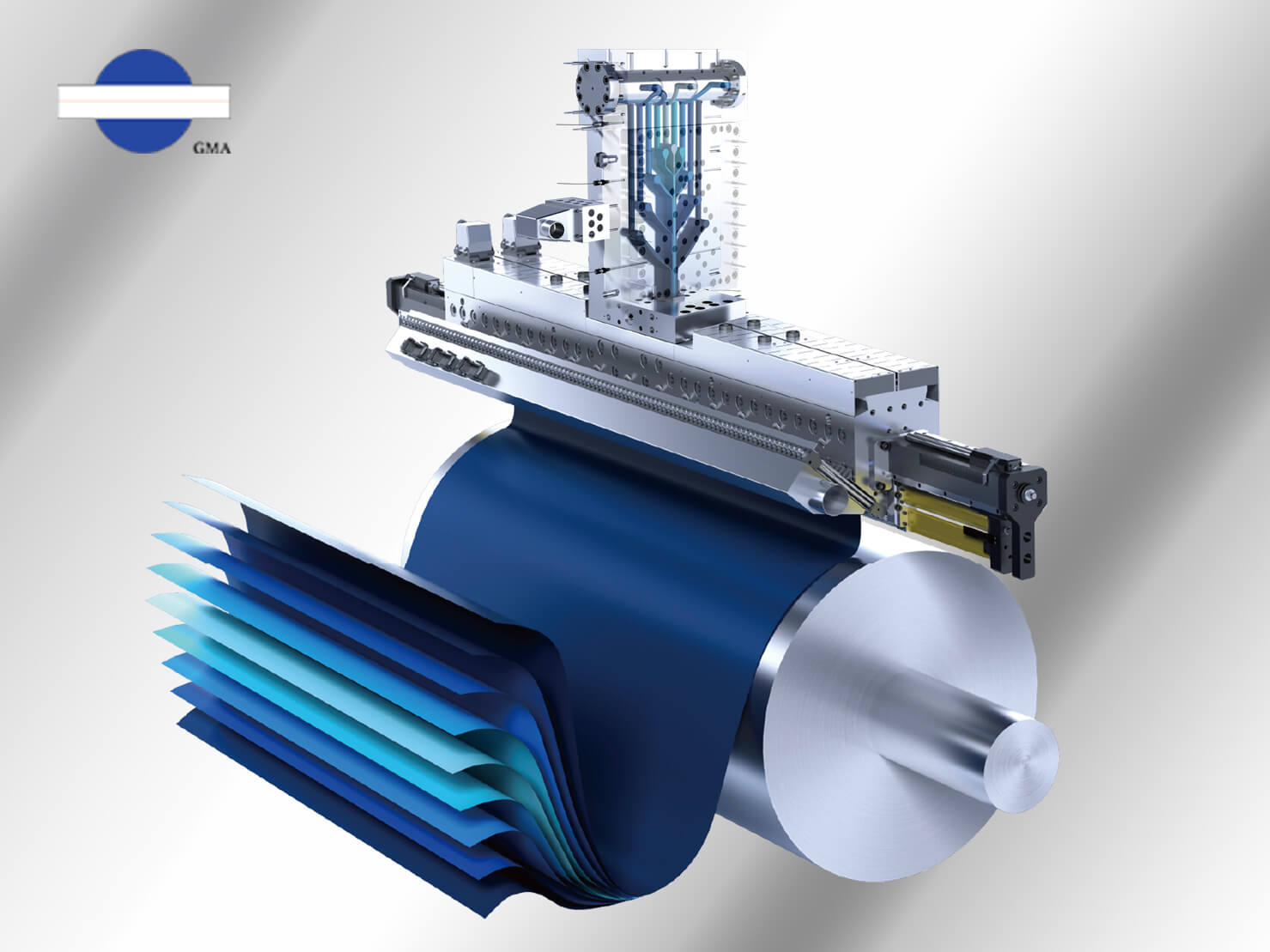
How Industrial AI Enhances Extrusion Die Design
Extrusion die design typically begins with CAE simulation. Engineers input material characteristics and relevant data to generate an initial flow-channel design. However, simulation software often removes real-world variables, meaning engineers must still rely on repeated trials, parameter adjustments, and experiential insights to refine the design.
This trial-and-error process is highly time-consuming. Industrial AI dramatically shortens this timeline by analyzing tens of thousands of historical die datasets. Through pattern recognition, AI identifies the optimal flow-channel configurations for specific materials and product types.

The most time-consuming part of simulation is the repetitive trial-and-error process.
Read More: Extrusion Die Design: From Theory to Practice
For example, PP materials can vary widely in MI values—from 1–40 (g/10 min) and in some cases reaching 1000. When engineers adjust one parameter, problems such as pressure imbalance or inconsistent flow rates may occur. With material rheology becoming increasingly complex, especially in multilayer structures, it is nearly impossible to manually extract reliable patterns from massive datasets.
AI bridges this gap by:
* Recognizing similar material behaviors
* Extracting proven design parameters
* Predicting machining tolerance impacts
* Providing optimized flow-channel geometries
As a result, simulation cycles are shortened, blind spots are minimized, and design accuracy increases. This represents the first and most fundamental application of AI in die engineering.

Supporting flow-channel design and mold-flow prediction is the primary core application of AI in die design and manufacturing.
Improving Die Manufacturing Through AI-Driven Process Control
High-quality Die design must be paired with high-quality machining. Precision extrusion dies require strict control over steel selection, machining processes, and tolerance management. Establishing a structured CNC database is the first step toward intelligent manufacturing.
With a complete data infrastructure, Industrial AI can support:
- Machining-accuracy analysis
- Parameter prediction
- Real-time error control
- Accurate machining-time forecasting
This level of intelligence reduces risk for operators with varying levels of experience and enhances overall machining stability. Electroplating processes can also be integrated into the database to further expand AI-driven quality control.

Using AI to support CNC process management enhances responsiveness and improves precision.
Read More: From Functional to Precision and Durability in Extrusion Dies — CNC × Electroplating × Polishing
From Automatic Dies to Truly Smart Dies
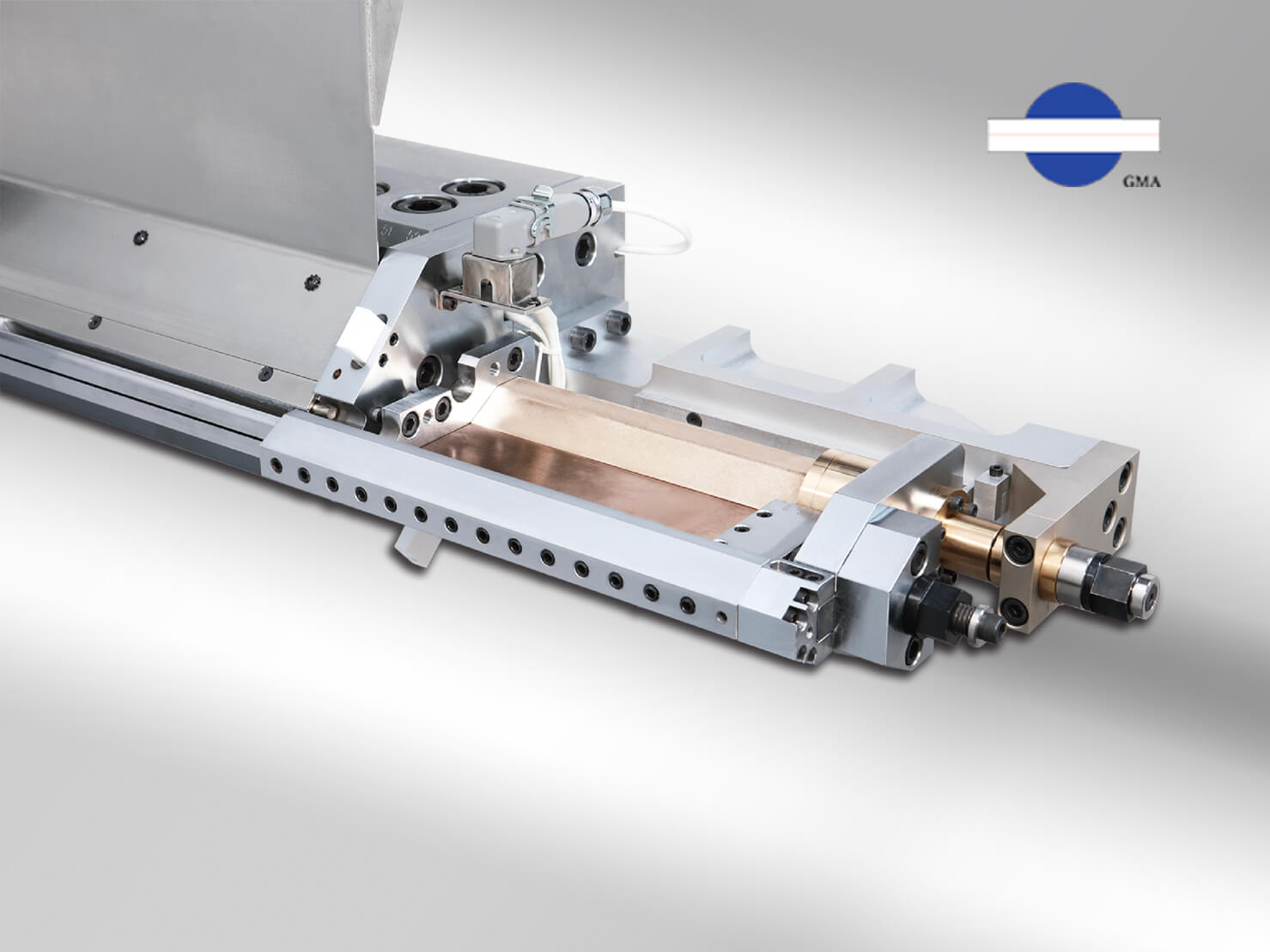
One of the most visible applications of AI in extrusion dies is automatic die technology. Traditional thermal-bolt systems—using heat expansion to adjust die-lip gaps—are widely known for improving product-thickness uniformity.
A more advanced system uses **micro-motor–driven bolts** is called MCAD , allowing highly precise adjustments based on predictive models. By combining production databases with AI algorithms, the system can automatically propose ideal die-lip settings and temperature adjustments in response to formulation or specification changes.
This minimizes trial time, reduces material waste, and elevates automatic dies into **next-generation smart precision dies**.

The micro-motor automatic control system (it is called MCAD) can be integrated with AI models, upgrading automatic dies into truly smart dies.
Read More: From Manual Adjustments to Automated Dies: Solving Precision and Waste
Toward Predictive and Transparent Die Lifecycle Management
Through the integration of Industrial AI, manufacturers can establish complete die design and production histories. This enables AI to:
- Predict part wear
- Recommend maintenance schedules
- Improve production readiness
- Reduce downtime caused by unexpected mold damage
For engineers, AI reduces repetitive workload and frees up time for innovation. For die users, AI offers shorter adjustment times, faster startup, more stable output, and enhanced long-term reliability.

In the future, AI will transform die manufacturing from an experience-driven process into a model-driven intelligent production system.
From Experience-Driven to Model-Driven
The Future of smart die Manufacturing, in the next era of competition, success will not be defined by who owns the most equipment, but by **who can extract the greatest intelligent value from their equipment**.
Industrial AI enables die design and manufacturing to become more predictable, transparent, and precise. It transforms the industry from “experience-driven decisions” to “model-driven intelligence.”
This shift does not diminish the importance of experience. Instead, it elevates the expertise of engineers by converting their knowledge into reusable, data-driven models that:
- Accelerate development
- Reduce risk
- Extend die lifespan
- Improve quality consistency
- Shorten lead time
- Increase overall productivity
AI is not here to replace people — it is here to amplify human potential.
When AI becomes the engineer’s most powerful partner, the era of manufacturing smart die truly begins.