Here are 10 key points to understand extrusion dies
2023.081. What is extrusion die
Due to different polymer properties and products design, there are derivative multi polymer process ways, such as injection, blown (also called blow molding), casting and extrusion.
Injection involves the injection of polymer material into a mold for shaping, used for products like toys and components for devices such as phones and tablets. On the other hand, blow molding maintains a hollow form by introducing air during the shaping process, commonly used for creating composite films and items like bottles and containers.
Extrusion remains a relatively unfamiliar field to most people, even those within the plastic industry. It can be challenging to grasp, despite being part of the plastic industry chain. Extrusion is comprised of two main categories: profile extrusion and flat extrusion. In profile extrusion, a screw extrudes polymer material into a mold, extending it for shaping, followed by cooling to set the form. This method is used for producing pipes for water or air, wires, and similar items.
Conversely, flat extrusion encompasses the continuous production of sheets, films, and laminated materials. This process involves distinct design and manufacturing of molds, whether it's for profile or flat extrusion. The following will provide a more detailed explanation of "flat extrusion die."

2. How extrusion die works?
The flat extrusion die, hereinafter referred to as the extrusion die, receives polymer material from a screw. It then guides the polymer through a chamber's channel, facilitating its extension and ensuring a uniform flow rate. Subsequently, the polymer exits the die to create a sheet or film of consistent thickness, which is then solidified through roller cooling to achieve the desired shape. In many cases, these sheets and films serve as intermediary products for further processing, enabling the production of various plastic items.

Extrusion dies are utilized in the production of sheets and films, although these intermediary materials are not the end plastic products consumers are familiar with. When compared to other methods of polymer shaping, the process of creating the final product, the extent of material loss in secondary processes, and the quality of the end product involve a multitude of intricate considerations. Designing an extrusion die involves an array of complexities, which is why only a limited number of suppliers specialize in this field. The development of extrusion dies demands a substantial investment in terms of equipment, labor, and resources, making it a challenging endeavor.
3. Structure of extrusion die
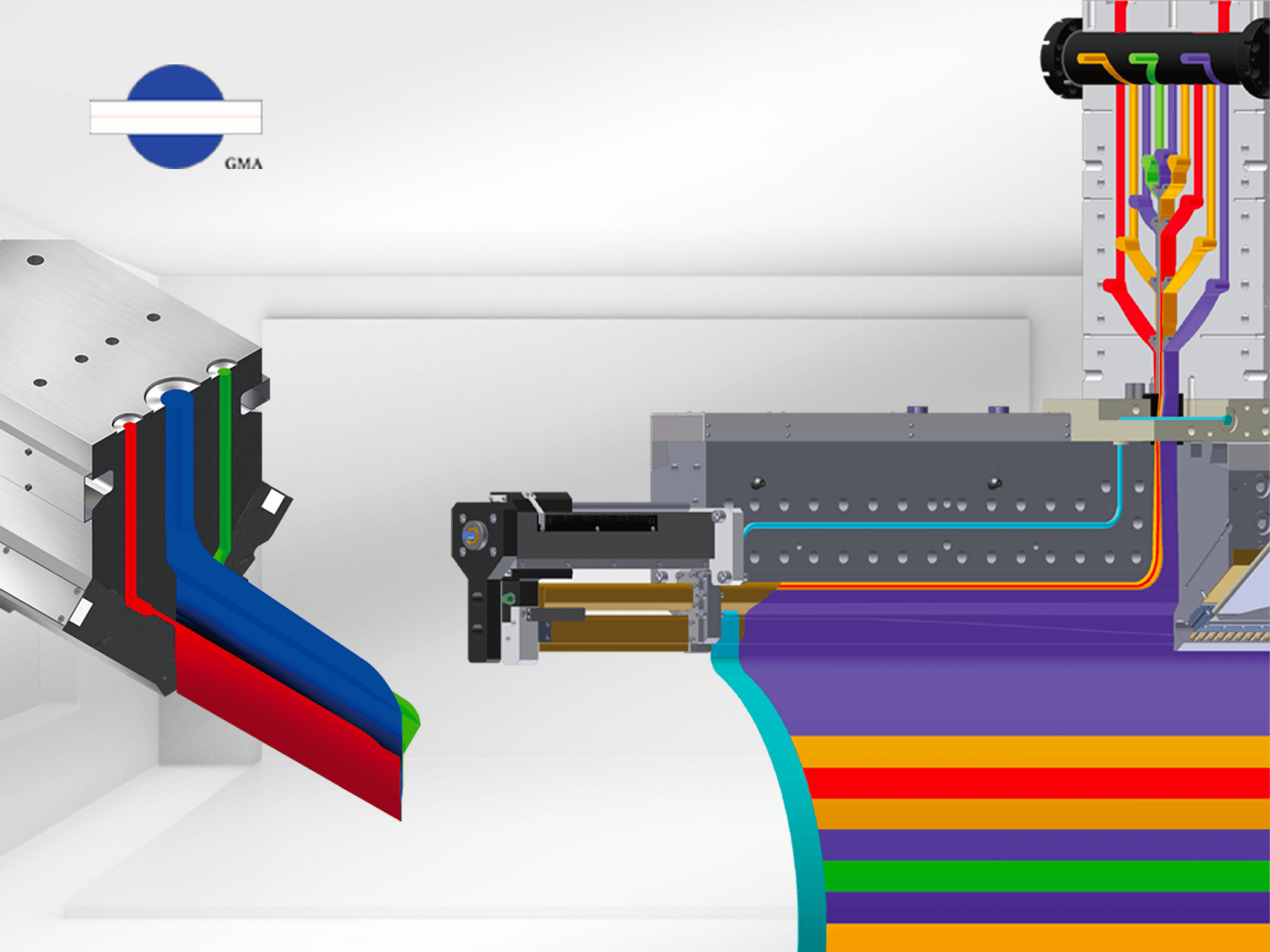
The fundamental structure of an extrusion die comprises three main components: the die body, the width adjusting system, and the thickness adjusting system. To accommodate varying polymer properties and processing methods such as CNC machining, grinding, and polishing, it is essential to carefully choose the appropriate steel for crafting the die body. The selection may involve different grades of mold steel or stainless steel, as the quality of die body processing directly influences the performance of the extrusion die.
.jpg?luf3wgfhvt)
The width adjusting system is designed to offer versatile adjustment options for the width of sheets or films. This includes both inner deckle and outer deckle mechanisms, while also ensuring user-friendly operation.
On the flip side, when it comes to adjusting thickness for wider ranges, in addition to the standard adjusting screws used to control the lip gap, options such as a rapid gap system or interchangeable lips become available, especially for thicker products.
4. Application of extrusion die
The extrusion die is used in sheet or film extrusion production lines. Sheets are used for various applications such as stationery boards, building materials (roofs, insulation panels), packaging boxes (for fruits and vegetables), and touch panels (diffusion plates, light guide boards), among others. Films are used in industrial packaging, plastic wraps for food, optical films, and automotive films, among other applications.

On the other hand, there are two types of extrusion dies used for combining two substances. One involves coating polymer onto paper or plastic film, using high temperature to bond the polymer and substrate together. This process is referred to as "lamination," and it utilizes a lamination die. Many paper cups or boxes, for example, have a thin PE layer coated on the surface for isolation. The Tetra Pak packaging is also produced using the lamination process.

5. Manufacturing of extrusion die
The process of extrusion die manufacturing includes CNC machining, grinding, polish, chrome plating, inspection and assembly. While it may appear straightforward, ensuring quality requires the presence of suitable equipment and quailed operators as the fundamental condition for each individual process. Furthermore, these processes are interdependent and closely linked to one another.
When discussing the design of the extrusion die channel, in addition to the main and sub channels, the section near the exit is referred to as the "landing area." In this region, the polymer remains for final elongation and transformation into a smooth sheet or film. Therefore, the landing area process is the essence of the extrusion die. Regardless of whether it involves surface grinding, mirror polishing, or chrome plating, precise calculations are necessary for each step of the process. As the die becomes wider, the complexity of the landing area process increases accordingly.

6.How to design extrusion die
Extrusion die design is influenced by the properties of the polymer being used. In today's landscape, consumer expectations for products are increasingly elevated, prompting polymer suppliers to develop new or modified polymers. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on incorporating recycled polymers to promote environmental friendliness. Manufacturers aim to showcase their product distinctiveness by crafting their own unique formulas. This might involve adding more recycled polymer or various additives, resulting in complex formulations that pose challenges for extrusion die design.
The primary role of an extrusion die is to facilitate uniform extension of polymer within the chamber, transforming it into a flat sheet or film. However, the complexity arises from the fact that the shape, depth, and curvature of the channel must be adjusted according to the specific properties of the polymer. While this process may appear straightforward, it presents a significant challenge.
Single-layer products often fail to meet consumer expectations, leading to the preference for multi-layer products (comprising more than two layers). Given the variations in polymer combinations, an alternative solution is the use of multi-manifold dies (featuring 2-5 channels) alongside the single-channel extrusion die.

In the present day, advanced simulation software can aid in optimizing the design of extrusion die channels. However, this software does not account for human factors and real-world variations. As a result, practical experience, encompassing both process knowledge and customer feedback, remains a crucial factor in the design of extrusion dies.
7. Maintainance of extrusion die
With proper operation and maintenance, and unless there are significant changes in product specifications or formulas, the average lifespan of an extrusion die is at least 5-10 years.
8.Advatange of extrusion die
In comparison to other polymer molds, extrusion dies are employed for high-capacity production, ranging from 200 kg to 2000 kg per hour. The design of the extrusion die, including the die body, width adjustment, and thickness adjustment systems, offers customers a broader range of options. This dispels common misconceptions and rigid perceptions of extrusion dies.
9. the market trend and forecast of extrusion die
The trends in extrusion die development can be summarized in two key points.
Firstly, there's a practical shift underway. The global plastic industry is actively promoting the "circular economy" as a response to environmental concerns. While many advocate for reduced plastic usage to combat pollution, it's important to recognize that there's currently no complete substitute for plastic. Thus, the real challenge lies in increasing the recycling rate of polymer materials and extending the lifespan of plastic products. In this context, optimizing extrusion die design becomes crucial. It enables customers to effectively utilize a higher percentage of recycled polymer, resulting in high-quality products. Whether customers seek to use modified materials or non-toxic plastics, the extrusion die plays a pivotal role in transforming polymers into tangible products.

Secondly, the application of new technology and innovation in extrusion die design is pivotal. Alongside advanced simulation systems that aid in extrusion die design, there's also a focus on converting processing data into visualizations for effective management. This involves the implementation of novel processing methods, their optimization, and a concurrent effort to minimize carbon emissions during the process. This collective approach ensures that extrusion dies are poised to meet a wider array of requirements and contribute to achieving the global net zero carbon emission goal in the future.
10. Extrusion die common issues
In the application of extrusion dies, common issues include die corrosion, design irregularities (resulting in unevenness), die lines, leakage, and die lip wear. Among these, thickness unevenness is a particularly critical concern. It often arises from inadequate channel design. By utilizing simulation analysis, solutions can be derived to modify the channel design and achieve improved outcomes.
Another significant issue is damage or wear. Considering both time and production costs, it's advisable to seek out manufacturers with the expertise to effectively repair extrusion dies. This approach is the most cost-effective way to ensure the extrusion die's performance is restored to its original level.
- Learn more: All extrusion die issue , let GMA help you.
Extrusion forming emerged in 1797, and since then, various other forming methods have been developed. While flat extrusion dies might not be widely recognized, they hold a significant and crucial position within the plastic industry.