What Exactly Is Coating? A Must-Read for Beginners! Quickly Dive into the World of Coating
2025.06.30Many people have heard of “coating,” but few truly understand how coating is applied—or how it can be used to improve product quality. With so many coating methods available, which one is truly the most suitable for your needs? Here are 10 key points to help you quickly uncover the secrets of the coating world!
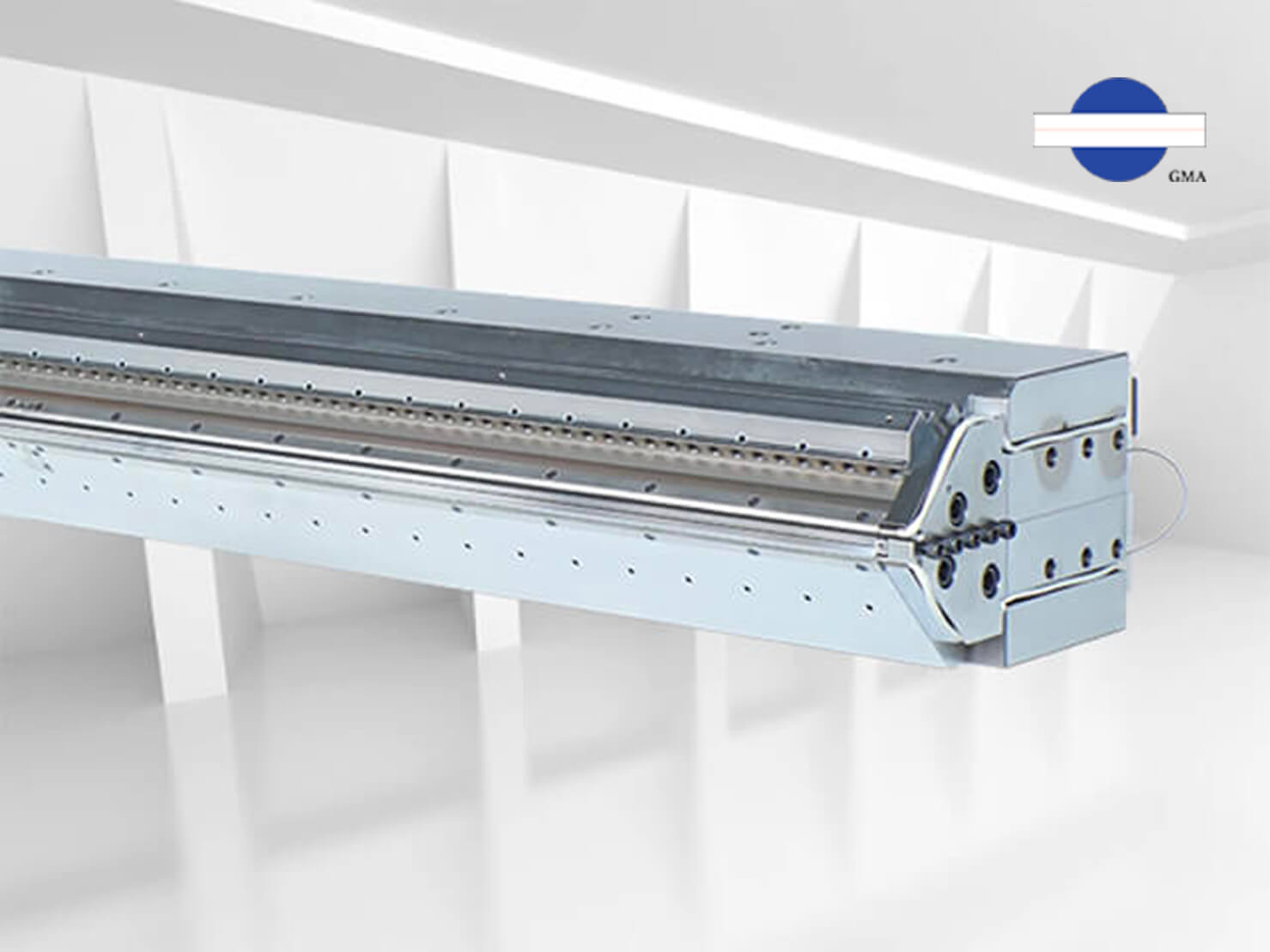
1. What is a Slot Die ?
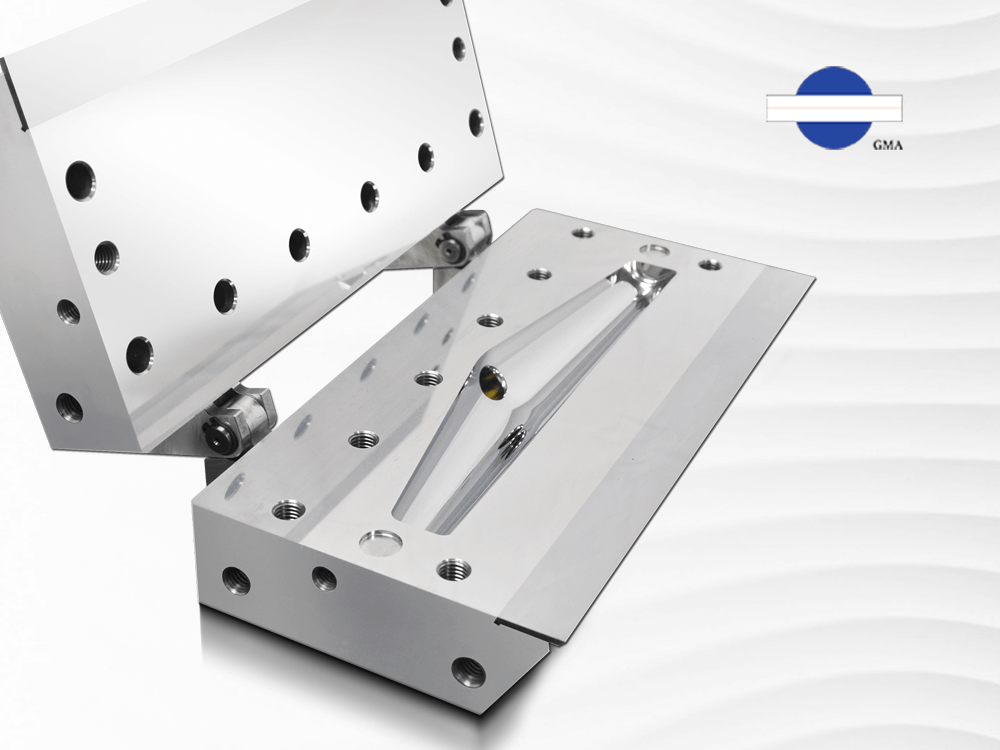
A slot die is a type of die used in high-precision coating processes. It gets its name from the narrow slit opening at the die lips. The design concept is similar to that of an extrusion die—material is pressurized and pushed into a die cavity, where it flows through a precisely engineered manifold that evenly distributes the fluid. This allows the coating liquid to be uniformly applied across the surface of a substrate. The result is a continuous, consistent coating layer with excellent uniformity.
2. What Are the Main Components of a Slot Die ?
The primary structure of a slot die includes the following components:
2.1 Manifold: Ensures even distribution of the coating liquid across the width of the die.
2.2 Die Lips: The opening through which the coating material exits; designed in various shapes to meet specific coating requirements.
2.3 Shim / Gap Adjustment Mechanism: Allows precise control of the coating thickness and width by adjusting the gap between the die lips.
 Slot dies are named
for the narrow slit opening at the die lips, and their internal flow channel
designs are simulated and optimized based on the specific properties of the
coating material.
Slot dies are named
for the narrow slit opening at the die lips, and their internal flow channel
designs are simulated and optimized based on the specific properties of the
coating material.
3What Are the Advantages of Slot Die ?
There are many coating methods used depending on specific applications and production needs, including roll coating, doctor blade coating, micro gravure, curtain coating, and spray coating. Among them, slot die coating is widely adopted due to the following key advantages:
3.1 High Precision – The die is precisely machined, allowing excellent control of coating thickness, with tolerances as tight as ±1 µm.
3.2 Wide Viscosity Compatibility – The internal manifold can be customized based on the viscosity of the coating liquid, making it suitable for both low and high viscosity materials.
3.3 Customizable Width – The die width can be tailored to meet coating width requirements, making it ideal for large-area, continuous coating processes.
3.4 Automation-Friendly – Slot die systems are easily integrated with automated production lines and support recipe-based parameter storage for consistent production.
Read more: From Principles to Applications: A Comprehensive Analysis of Slot Die Coating
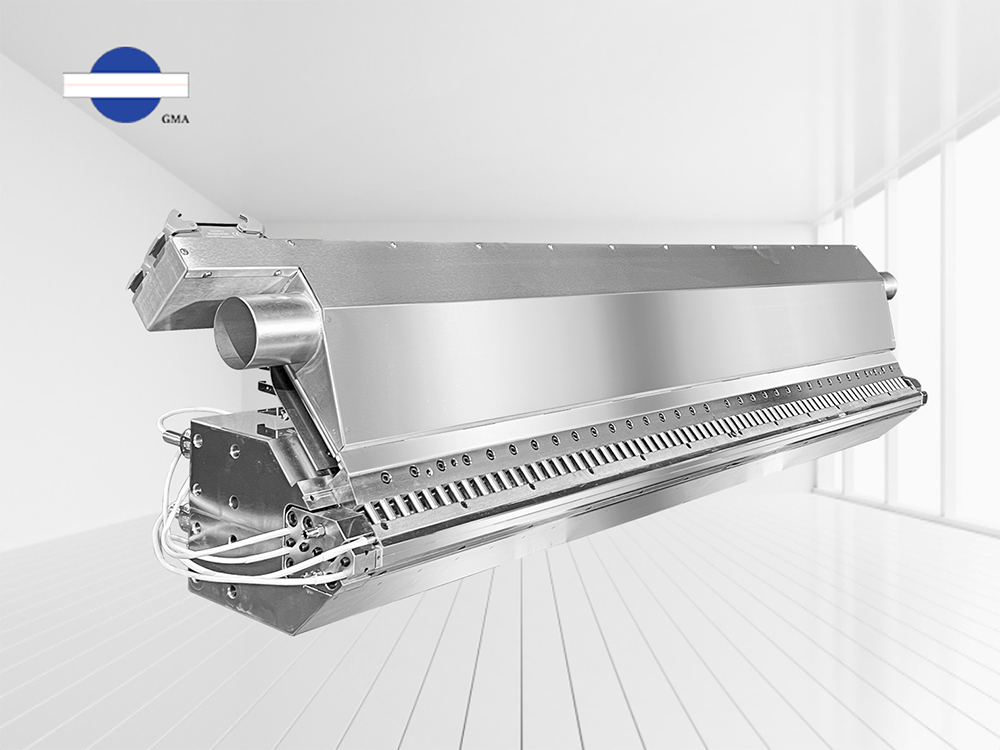
4. What Is a Roll-to-Roll Coating Machine?
Roll-to-Roll (R2R) coating is a continuous manufacturing process in which flexible materials—such as PET, PI, or copper foil—are fed into the system in roll form. The substrate undergoes a series of steps including coating, drying, and cooling, and is then rewound into a roll. This uninterrupted process enables high production efficiency and is ideal for large-scale, continuous coating applications.
5. What Are the Basic Components of a Roll-to-Roll Coating Machine?
5.1 Unwinding Unit – Holds and feeds the base material (substrate) into the coating line in roll form.
5.2 Coating Station – Can be equipped with a single slot die or a multi-functional coating head. The latter allows flexibility to switch between different methods, such as slot die, comma roll, or micro gravure coating, based on process requirements.
5.3 Drying Oven – Tailored to the coating material and solvent type. Common drying methods include thermal oil heating, hot air drying, and, for certain specialty coatings, far-infrared or UV curing.
5.4 Rewinding Unit – Collects the coated and dried substrate back into a roll for further processing or packaging.
Optional add-on units can be integrated depending on process needs, such as:
Lamination units / Release film handling / Automated die systems / Thickness measurement devices / Surface treatment equipment (e.g., corona or plasma treatment) etc.
 A roll-to-roll coating machine typically consists
of an unwinding unit, a coating station, a drying oven, and a rewinding unit.
A roll-to-roll coating machine typically consists
of an unwinding unit, a coating station, a drying oven, and a rewinding unit.
What Are the Key Advantages of Roll-to-Roll Coating Machines?
Roll-to-Roll (R2R) coating systems are widely used across many industries due to the following major advantages:
6.1 Continuous & Efficient Production – Ideal for high-volume manufacturing, as the process runs uninterrupted.
6.2 Customizable Drying Zones – Drying ovens can be tailored to specific coating formulations, making it easy to handle materials that require multi-stage or gradual drying.
6.3 Easy Integration with Automation – R2R systems are well-suited for automated process control and real-time quality monitoring.
6.4 Flexible & Customizable Design – The machine can be configured to handle a variety of coating processes and product types on the same platform.
Read more: The Ultimate Craft Hidden in Daily Life: A Journey Through Roll-to-Roll Coating Technology
7. Why Are Slot Dies and Roll-to-Roll Coating Machines the Perfect Coating Duo?
Slot dies are almost always used in roll-to-roll (R2R) coating systems—and for good reason. They complement each other perfectly, with the following advantages:
7.1 Precise Coating Uniformity – Slot dies allow for excellent control of coating thickness and distribution, making them ideal for continuous production lines.
7.2 Designed for Continuous Operation – R2R systems are built for nonstop production and can accommodate a wide range of production speeds based on process requirements.
7.3 Tight Control of Key Parameters – When slot dies are paired with R2R systems, critical coating parameters can be precisely managed to ensure high-quality, consistent output. These parameters include:
Web speed/ Coating pressure and flow rate/ Die lip gap (coating thickness)/ Web tension and temperature etc.
8. In Which Industries Are Slot Die and Roll-to-Roll Technologies Used?
Slot die coating and roll-to-roll (R2R) processing technologies have been widely adopted across numerous industries due to their precision and scalability. Key application areas include:
|
Industry |
Application Examples |
|
Lithium Batteries |
Electrode coating, separator film coating |
|
Semiconductors |
Photoresist coating, conductive adhesive application |
|
Optical and displays |
Brightness enhancement films, anti-fingerprint layers, anti-glare coatings |
|
Solar Energy |
Back sheet coatings, encapsulation layers, hydrophobic films |
|
Medical & Sensors |
Biosensor membranes, drug delivery films |
|
Automotive & Others |
Window films, paint protective films(PPF), product labels |
Read more: Enhance PPF Quality: Focus on TPU Film Coating Production and Composition
9. How to Evaluate the Implementation of Coating Technology?
Before introducing coating technology into your production process, it's important to assess the following factors to ensure success:
9.1 Evaluate Product Requirements – Determine the desired coating thickness and uniformity standards.
9.2 Analyze Coating Material Properties – Understand the viscosity and rheological behavior of the coating fluid.
9.3 Conduct Trial Coating – Use a lab-scale or pilot machine to perform trial runs and verify process feasibility.
9.4 Review Production Needs – Confirm the required web speed and drying conditions for full-scale production.
9.5 Choose the Right Partners – Work with experienced die and equipment suppliers who can offer tailored solutions.
9.6 Plan the Facility Layout – Ensure your production space is suitable for coating line integration, including utilities and environmental control.
9.7 Train Operators – Provide adequate training for staff to ensure safe and effective operation of the coating equipment.
 When evaluating the implementation of a coating
process, it is advisable to first conduct trial coating and related tests using
a lab-scale or pilot machine.
When evaluating the implementation of a coating
process, it is advisable to first conduct trial coating and related tests using
a lab-scale or pilot machine.
10. How Long Does It Take to See Returns After Investing in Coating Equipment?
The timeline for seeing tangible results from investing in coating equipment varies for each investor, but several key factors play a role in determining how soon benefits can be realized:
10.1 Market and Distribution Channels – The more control and understanding you have of your target market and distribution channels, the easier it is to introduce coated products and achieve returns.
10.2 Coating Technology Expertise – Familiarity with coating formulations and process know-how can significantly improve product quality and speed up optimization.
10.3 Cost and Risk Management – A clear understanding of all associated costs—such as coating materials, equipment investment, labor, and facility setup—is essential.
More importantly, risk control is critical:
How long will it take to transition from installation to mass production?
Can the purchased equipment deliver the required product quality?
Is there sufficient technical support and added value from the equipment provider?
Well-managed execution of these aspects will accelerate the path to return on investment.
The Core of Coating Technology: Precision and Stability
From process optimization to yield improvement, coating technology has evolved from a supporting role into a key driver of product performance and manufacturing efficiency. Whether utilizing the optimal combination of slot die and roll-to-roll equipment, or exploring other methods like punch (sheet to sheet) coating, the rapid advancements in coating technology reflect the growing demand among manufacturers to move toward high-end production.
Coating excellence cannot be achieved overnight—it requires time, experience, and continuous improvement. The sooner a company begins its coating journey, the greater the advantage it gains in staying ahead of the competition.
 Coating technology is a pathway to high-end
manufacturing, but it cannot be mastered in a short time—the earlier you start,
the better advantage you gain.
Coating technology is a pathway to high-end
manufacturing, but it cannot be mastered in a short time—the earlier you start,
the better advantage you gain.